Press Release
Sharper and Deeper Views with MACAO-VLTI
"First Light" with Powerful Adaptive Optics System for the VLT Interferometer
13 May 2003
On April 18, 2003, a team of engineers from ESO celebrated the successful accomplishment of "First Light" for the MACAO-VLTI Adaptive Optics facility on the Very Large Telescope (VLT) at the Paranal Observatory (Chile). This is the second Adaptive Optics (AO) system put into operation at this observatory, following the NACO facility. The achievable image sharpness of a ground-based telescope is normally limited by the effect of atmospheric turbulence. However, with Adaptive Optics (AO) techniques, this major drawback can be overcome so that the telescope produces images that are as sharp as theoretically possible, i.e., as if they were taken from space. The acronym "MACAO" stands for "Multi Application Curvature Adaptive Optics" which refers to the particular way optical corrections are made which "eliminate" the blurring effect of atmospheric turbulence. The MACAO-VLTI facility was developed at ESO. It is a highly complex system of which four, one for each 8.2-m VLT Unit Telescope, will be installed below the telescopes (in the Coudé rooms). These systems correct the distortions of the light beams from the large telescopes (induced by the atmospheric turbulence) before they are directed towards the common focus at the VLT Interferometer (VLTI). The installation of the four MACAO-VLTI units of which the first one is now in place, will amount to nothing less than a revolution in VLT interferometry. An enormous gain in efficiency will result, because of the associated 100-fold gain in sensitivity of the VLTI. Put in simple words, with MACAO-VLTI it will become possible to observe celestial objects 100 times fainter than now . Soon the astronomers will be thus able to obtain interference fringes with the VLTI of a large number of objects hitherto out of reach with this powerful observing technique, e.g. external galaxies. The ensuing high-resolution images and spectra will open entirely new perspectives in extragalactic research and also in the studies of many faint objects in our own galaxy, the Milky Way. During the present period, the first of the four MACAO-VLTI facilties was installed, integrated and tested by means of a series of observations. For these tests, an infrared camera was specially developed which allowed a detailed evaluation of the performance. It also provided some first, spectacular views of various celestial objects, some of which are shown here.
MACAO - the Multi Application Curvature Adaptive Optics facility
Adaptive Optics (AO) systems work by means of a computer-controlled deformable mirror (DM) that counteracts the image distortion induced by atmospheric turbulence. It is based on real-time optical corrections computed from image data obtained by a "wavefront sensor" (a special camera) at very high speed, many hundreds of times each second.
The ESO Multi Application Curvature Adaptive Optics (MACAO) system uses a 60-element bimorph deformable mirror (DM) and a 60-element curvature wavefront sensor, with a "heartbeat" of 350 Hz (times per second). With this high spatial and temporal correcting power, MACAO is able to nearly restore the theoretically possible ("diffraction-limited") image quality of an 8.2-m VLT Unit Telescope in the near-infrared region of the spectrum, at a wavelength of about 2 µm. The resulting image resolution (sharpness) of the order of 60 milli-arcsec is an improvement by more than a factor of 10 as compared to standard seeing-limited observations. Without the benefit of the AO technique, such image sharpness could only be obtained if the telescope were placed above the Earth's atmosphere.
The technical development of MACAO-VLTI in its present form was begun in 1999 and with project reviews at 6 months' intervals, the project quickly reached cruising speed. The effective design is the result of a very fruitful collaboration between the AO department at ESO and European industry which contributed with the diligent fabrication of numerous high-tech components, including the bimorph DM with 60 actuators, a fast-reaction tip-tilt mount and many others. The assembly, tests and performance-tuning of this complex real-time system was assumed by ESO-Garching staff.
Installation at Paranal
The first crates of the 60+ cubic-meter shipment with MACAO components arrived at the Paranal Observatory on March 12, 2003. Shortly thereafter, ESO engineers and technicians began the painstaking assembly of this complex instrument, below the VLT 8.2-m KUEYEN telescope (formerly UT2).
They followed a carefully planned scheme, involving installation of the electronics, water cooling systems, mechanical and optical components. At the end, they performed the demanding optical alignment, delivering a fully assembled instrument one week before the planned first test observations. This extra week provided a very welcome and useful opportunity to perform a multitude of tests and calibrations in prepration of the actual observations.
AO to the service of Interferometry
The VLT Interferometer (VLTI) combines starlight captured by two or more 8.2- VLT Unit Telescopes (later also from four moveable1.8-m Auxiliary Telescopes) and allows to vastly increase the image resolution. The light beams from the telescopes are brought together "in phase" (coherently). Starting out at the primary mirrors, they undergo numerous reflections along their different paths over total distances of several hundred meters before they reach the interferometric Laboratory where they are combined to within a fraction of a wavelength, i.e., within nanometers!
The gain by the interferometric technique is enormous - combining the light beams from two telescopes separated by 100 metres allows observation of details which could otherwise only be resolved by a single telescope with a diameter of 100 metres. Sophisticated data reduction is necessary to interpret interferometric measurements and to deduce important physical parameters of the observed objects like the diameters of stars, etc.
The VLTI measures the degree of coherence of the combined beams as expressed by the contrast of the observed interferometric fringe pattern. The higher the degree of coherence between the individual beams, the stronger is the measured signal. By removing wavefront aberrations introduced by atmospheric turbulence, the MACAO-VLTI systems enormously increase the efficiency of combining the individual telescope beams.
In the interferometric measurement process, the starlight must be injected into optical fibers which are extremely small in order to accomplish their function; only 6 µm (0.006 mm) in diameter. Without the "refocussing" action of MACAO, only a tiny fraction of the starlight captured by the telescopes can be injected into the fibers and the VLTI would not be working at the peak of efficiency for which it has been designed.
MACAO-VLTI will now allow a gain of a factor 100 in the injected light flux - this will be tested in detail when two VLT Unit Telescopes, both equipped with MACAO-VLTI's, work together. However, the very good performance actually achieved with the first system makes the engineers very confident that a gain of this order will indeed be reached. This ultimate test will be performed as soon as the second MACAO-VLTI system has been installed later this year.
MACAO-VLTI First Light
After one month of installation work and following tests by means of an artificial light source installed in the Nasmyth focus of KUEYEN, MACAO-VLTI had "First Light" on April 18 when it received "real" light from several astronomical obejcts.
During the preceding performance tests to measure the image improvement (sharpness, light energy concentration) in near-infrared spectral bands at 1.2, 1.6 and 2.2 µm, MACAO-VLTI was checked by means of a custom-made Infrared Test Camera developed for this purpose by ESO. This intermediate test was required to ensure the proper functioning of MACAO before it is used to feed a corrected beam of light into the VLTI.
After only a few nights of testing and optimizing of the various functions and operational parameters, MACAO-VLTI was ready to be used for astronomical observations. The images below were taken under average seeing conditions and illustrate the improvement of the image quality when using MACAO-VLTI.
MACAO-VLTI - First Images
Here are some of the first images obtained with the test camera at the first MACAO-VLTI system, now installed at the 8.2-m VLT KUEYEN telescope.
Image eso0313c show the first image in the infrared K-band (wavelength 2.2 µm) of a star (visual magnitude 10) obtained without and with image corrections by means of adaptive optics.
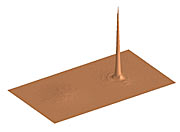
ESO Press Photo eso0313 displays one of the best images obtained with MACAO-VLTI during the early tests. It shows a Strehl ratio (measure of light concentration) that fulfills the specifications according to which MACAO-VLTI was built. This enormous improvement when using AO techniques is clearly demonstrated in ESO Press Photo eso0313, with the uncorrected image profile (left) hardly visible when compared to the corrected profile (right).
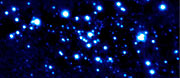
ESO Press Photo eso0312 demonstrates the correction capabilities of MACAO-VLTI when using a faint guide star. Tests using different spectral types showed that the limiting visual magnitude varies between 16 for early-type B-stars and about 18 for late-type M-stars.
Astronomical Objects seen at the Diffraction Limit
The following examples of MACAO-VLTI observations of two well-known astronomical objects were obtained in order to provisionally evaluate the research opportunities now opening with MACAO-VLTI. They may well be compared with space-based images.
The Galactic Center
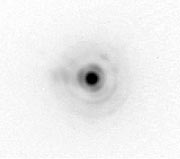
The center of our own galaxy is located in the Sagittarius constellation at a distance of approximately 30,000 light-years. ESO Press Photo eso0313 shows a short-exposure infrared view of this region, obtained by MACAO-VLTI during the early test phase.
Recent AO observations using the NACO facility at the VLT provide compelling evidence that a supermassive black hole with 2.6 million solar masses is located at the very center. This result, based on astrometric observations of a star orbiting the black hole and approaching it to within a distance of only 17 light-hours, would not have been possible without images of diffraction limited resolution.
Eta Carinae
Eta Carinae is one of the heaviest stars known, with a mass that probably exceeds 100 solar masses. It is about 4 million times brighter than the Sun, making it one of the most luminous stars known.
Such a massive star has a comparatively short lifetime of about 1 million years only and - measured in the cosmic timescale- Eta Carinae must have formed quite recently. This star is highly unstable and prone to violent outbursts. They are caused by the very high radiation pressure at the star's upper layers, which blows significant portions of the matter at the "surface" into space during violent eruptions that may last several years. The last of these outbursts occurred between 1835 and 1855 and peaked in 1843. Despite its comparaticely large distance - some 7,500 to 10,000 light-years - Eta Carinae briefly became the second brightest star in the sky at that time (with an apparent magnitude -1), only surpassed by Sirius.
Frosty Leo
Frosty Leo is a magnitude 11 (post-AGB) star surrounded by an envelope of gas, dust, and large amounts of ice (hence the name). The associated nebula is of "butterfly" shape (bipolar morphology) and it is one of the best known examples of the brief transitional phase between two late evolutionary stages, asymptotic giant branch (AGB) and the subsequent planetary nebulae (PNe).
For a three-solar-mass object like this one, this phase is believed to last only a few thousand years, the wink of an eye in the life of the star. Hence, objects like this one are very rare and Frosty Leo is one of the nearest and brightest among them.
Contacts
Norbert Hubin
ESO
Garching, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200-6517
Email: nhubin@eso.org
Robin Arsenault
ESO
Garching, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200-6524
Email: rarsenau@eso.org
Markus Kasper
ESO
Garching, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200-6359
Email: mkasper@eso.org
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso0313 |
| Legacy ID: | PR 11/03 |
| Name: | Eta Carinae, First Light, Frosty Leo, HIC 59206 , HIC 69495, HIC 74324, Instrumentation, MACAO |
| Type: | Unspecified : Technology : Observatory : Telescope |
| Facility: | Very Large Telescope Interferometer |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.