Press Release
New image reveals secrets of planet birth
25 July 2023

A spectacular new image released today by the European Southern Observatory gives us clues about how planets as massive as Jupiter could form. Using ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), researchers have detected large dusty clumps, close to a young star, that could collapse to create giant planets.
“This discovery is truly captivating as it marks the very first detection of clumps around a young star that have the potential to give rise to giant planets,” says Alice Zurlo, a researcher at the Universidad Diego Portales, Chile, involved in the observations.
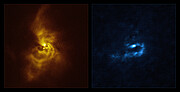
The work is based on a mesmerising picture obtained with the Spectro-Polarimetric High-contrast Exoplanet REsearch (SPHERE) instrument on ESO’s VLT that features fascinating detail of the material around the star V960 Mon. This young star is located over 5000 light-years away in the constellation Monoceros and attracted astronomers’ attention when it suddenly increased its brightness more than twenty times in 2014. SPHERE observations taken shortly after the onset of this brightness ‘outburst’ revealed that the material orbiting V960 Mon is assembling together in a series of intricate spiral arms extending over distances bigger than the entire Solar System.
This finding then motivated astronomers to analyse archive observations of the same system made with ALMA, in which ESO is a partner. The VLT observations probe the surface of the dusty material around the star, while ALMA can peer deeper into its structure. “With ALMA, it became apparent that the spiral arms are undergoing fragmentation, resulting in the formation of clumps with masses akin to those of planets,” says Zurlo.
Astronomers believe that giant planets form either by ‘core accretion’, when dust grains come together, or by ‘gravitational instability’, when large fragments of the material around a star contract and collapse. While researchers have previously found evidence for the first of these scenarios, support for the latter has been scant.
“No one had ever seen a real observation of gravitational instability happening at planetary scales — until now,” says Philipp Weber, a researcher at the University of Santiago, Chile, who led the study published today in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
“Our group has been searching for signs of how planets form for over ten years, and we couldn't be more thrilled about this incredible discovery,” says team-member Sebastián Pérez from the University of Santiago, Chile.
ESO instruments will help astronomers unveil more details of this captivating planetary system in the making, and ESO’s Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) will play a key role. Currently under construction in Chile’s Atacama Desert, the ELT will be able to observe the system in greater detail than ever before, collecting crucial information about it. “The ELT will enable the exploration of the chemical complexity surrounding these clumps, helping us find out more about the composition of the material from which potential planets are forming,” concludes Weber.
More information
The team behind this work comprises young researchers from diverse Chilean universities and institutes, under the Millennium Nucleus on Young Exoplanets and their Moons (YEMS) research centre, funded by the Chilean National Agency for Research and Development (ANID) and its Millennium Science Initiative Program. The two facilities used, ALMA and VLT, are located in Chile’s Atacama Desert.
This research is presented in a paper to appear in The Astrophysical Journal Letters (doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/ace186).
The team is composed of P. Weber (Departamento de Física, Universidad de Santiago de Chile, Chile [USACH]; Millennium Nucleus on Young Exoplanets and their Moons, Chile [YEMS]; Center for Interdisciplinary Research in Astrophysics and Space Exploration, Universidad de Santiago de Chile, Chile [CIRAS]), S. Pérez (USACH; YEMS; CIRAS), A. Zurlo (YEMS; Núcleo de Astronomía, Universidad Diego Portales Chile [UDP]; Escuela de Ingeniería Industrial, Universidad Diego Portales, Chile), J. Miley (Joint ALMA Observatory, Chile; National Astronomical Observatory of Japan, Japan), A. Hales (National Radio Astronomy Observatory, USA), L. Cieza (YEMS; UDP), D. Principe (MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research, USA), M. Cárcamo (YEMS; CIRAS; USACH, Faculty of Engineering, Computer Engineering Department, Chile), A. Garufi (INAF, Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Italy), Á. Kóspál (Konkoly Observatory, Research Centre for Astronomy and Earth Sciences, Eötvös Loránd Research Network (ELKH), Hungary; CSFK, MTA Centre of Excellence, Hungary; ELTE Eötvös Loránd University, Institute of Physics, Hungary; Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Germany), M. Takami (Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, Taiwan, ROC), J. Kastner (School of Physics & Astronomy, Rochester Institute of Technology, USA), Z. Zhu (Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Nevada, USA; Nevada Center for Astrophysics, University of Nevada, USA), and J. Williams (Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawai‘i at Manoa, USA).
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of ESO, the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) and the National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS) of Japan in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. ALMA is funded by ESO on behalf of its Member States, by NSF in cooperation with the National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and the National Science and Technology Council (NSTC) in Taiwan and by NINS in cooperation with the Academia Sinica (AS) in Taiwan and the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI). ALMA construction and operations are led by ESO on behalf of its Member States; by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), managed by Associated Universities, Inc. (AUI), on behalf of North America; and by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) on behalf of East Asia. The Joint ALMA Observatory (JAO) provides the unified leadership and management of the construction, commissioning and operation of ALMA.
The European Southern Observatory (ESO) enables scientists worldwide to discover the secrets of the Universe for the benefit of all. We design, build and operate world-class observatories on the ground — which astronomers use to tackle exciting questions and spread the fascination of astronomy — and promote international collaboration for astronomy. Established as an intergovernmental organisation in 1962, today ESO is supported by 16 Member States (Austria, Belgium, Czechia, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom), along with the host state of Chile and with Australia as a Strategic Partner. ESO’s headquarters and its visitor centre and planetarium, the ESO Supernova, are located close to Munich in Germany, while the Chilean Atacama Desert, a marvellous place with unique conditions to observe the sky, hosts our telescopes. ESO operates three observing sites: La Silla, Paranal and Chajnantor. At Paranal, ESO operates the Very Large Telescope and its Very Large Telescope Interferometer, as well as survey telescopes such as VISTA. Also at Paranal ESO will host and operate the Cherenkov Telescope Array South, the world’s largest and most sensitive gamma-ray observatory. Together with international partners, ESO operates ALMA on Chajnantor, a facility that observes the skies in the millimetre and submillimetre range. At Cerro Armazones, near Paranal, we are building “the world’s biggest eye on the sky” — ESO’s Extremely Large Telescope. From our offices in Santiago, Chile we support our operations in the country and engage with Chilean partners and society.
Links
- Research paper
- Photos of the VLT
- Photos of ALMA
- Find out more about ESO's Extremely Large Telescope
- For journalists: subscribe to receive our releases under embargo in your language
- For scientists: got a story? Pitch your research
Contacts
Philipp Weber
University of Santiago
Santiago, Chile
Cell: +56966821513 / +4915759366702
Email: philipppweber@gmail.com
Alice Zurlo
Universidad Diego Portales
Santiago, Chile
Tel: +56 22138153
Email: alice.zurlo@mail.udp.cl
Sebastián Pérez
University of Santiago
Santiago, Chile
Cell: +56 9 78776812
Email: sebastian.perez.ma@usach.cl
Bárbara Ferreira
ESO Media Manager
Garching bei München, Germany
Tel: +49 89 3200 667
Cell: +49 151 241 664 00
Email: press@eso.org
About the Release
| Release No.: | eso2312 |
| Name: | V960 Mon |
| Type: | Milky Way : Star : Circumstellar Material : Disk : Protoplanetary |
| Facility: | Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array, Very Large Telescope |
| Instruments: | SPHERE |
| Science data: | 2023ApJ...952L..17W |
Our use of Cookies
We use cookies that are essential for accessing our websites and using our services. We also use cookies to analyse, measure and improve our websites’ performance, to enable content sharing via social media and to display media content hosted on third-party platforms.
ESO Cookies Policy
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere (ESO) is the pre-eminent intergovernmental science and technology organisation in astronomy. It carries out an ambitious programme focused on the design, construction and operation of powerful ground-based observing facilities for astronomy.
This Cookies Policy is intended to provide clarity by outlining the cookies used on the ESO public websites, their functions, the options you have for controlling them, and the ways you can contact us for additional details.
What are cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit. They serve various purposes, such as remembering login credentials and preferences and enhance your browsing experience.
Categories of cookies we use
Essential cookies (always active): These cookies are strictly necessary for the proper functioning of our website. Without these cookies, the website cannot operate correctly, and certain services, such as logging in or accessing secure areas, may not be available; because they are essential for the website’s operation, they cannot be disabled.
Functional Cookies: These cookies enhance your browsing experience by enabling additional features and personalization, such as remembering your preferences and settings. While not strictly necessary for the website to function, they improve usability and convenience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent.
Analytics cookies: These cookies collect information about how visitors interact with our website, such as which pages are visited most often and how users navigate the site. This data helps us improve website performance, optimize content, and enhance the user experience; these cookies are only placed if you provide your consent. We use the following analytics cookies.
Matomo Cookies:
This website uses Matomo (formerly Piwik), an open source software which enables the statistical analysis of website visits. Matomo uses cookies (text files) which are saved on your computer and which allow us to analyze how you use our website. The website user information generated by the cookies will only be saved on the servers of our IT Department. We use this information to analyze www.eso.org visits and to prepare reports on website activities. These data will not be disclosed to third parties.
On behalf of ESO, Matomo will use this information for the purpose of evaluating your use of the website, compiling reports on website activity and providing other services relating to website activity and internet usage.
Matomo cookies settings:
Additional Third-party cookies on ESO websites: some of our pages display content from external providers, e.g. YouTube.
Such third-party services are outside of ESO control and may, at any time, change their terms of service, use of cookies, etc.
YouTube: Some videos on the ESO website are embedded from ESO’s official YouTube channel. We have enabled YouTube’s privacy-enhanced mode, meaning that no cookies are set unless the user actively clicks on the video to play it. Additionally, in this mode, YouTube does not store any personally identifiable cookie data for embedded video playbacks. For more details, please refer to YouTube’s embedding videos information page.
Cookies can also be classified based on the following elements.
Regarding the domain, there are:
- First-party cookies, set by the website you are currently visiting. They are stored by the same domain that you are browsing and are used to enhance your experience on that site;
- Third-party cookies, set by a domain other than the one you are currently visiting.
As for their duration, cookies can be:
- Browser-session cookies, which are deleted when the user closes the browser;
- Stored cookies, which stay on the user's device for a predetermined period of time.
How to manage cookies
Cookie settings: You can modify your cookie choices for the ESO webpages at any time by clicking on the link Cookie settings at the bottom of any page.
In your browser: If you wish to delete cookies or instruct your browser to delete or block cookies by default, please visit the help pages of your browser:
Please be aware that if you delete or decline cookies, certain functionalities of our website may be not be available and your browsing experience may be affected.
You can set most browsers to prevent any cookies being placed on your device, but you may then have to manually adjust some preferences every time you visit a site/page. And some services and functionalities may not work properly at all (e.g. profile logging-in, shop check out).
Updates to the ESO Cookies Policy
The ESO Cookies Policy may be subject to future updates, which will be made available on this page.
Additional information
For any queries related to cookies, please contact: pdprATesoDOTorg.
As ESO public webpages are managed by our Department of Communication, your questions will be dealt with the support of the said Department.